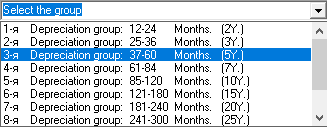
1. First of all, let's go to the investment plan and enter the form of planning and accounting for assets (line "fixed assets and other assets"). In this form, you must select a depreciation group before adding, deleting, or editing an asset. You can choose from the list one of 10 depreciation groups or choose "non-depreciable assets".
☛ Depreciation groups differ from each other by the depreciation period. Non-depreciable assets are those assets that cannot be depreciated - land, building, structures, etc.
See the table "Depreciation groups". For information on how to set the depreciation coefficients for depreciation groups in the settings, see the help section "General settings. Depreciation".
2. After the depreciation group has been selected, you can add a new asset (edit menu "add" or F2) and start editing the asset.
☛ Assets are edited in 7 tabs, depending on transactions with assets, these are receipts, accounting, depreciation, modernization, revaluation, conservation and disposal. In the last tab “table of residual value” you can see the result of the calculation for this asset.
3. In the “receipt” tab, you need to select the type of asset (fixed asset, intangible or investment asset) and the method of receipt (purchase, shareholder contribution or other receipts). Also, in the lists, you need to select the periods of receipt and registration, indicate the period of useful and actual use, and also, if necessary, indicate the accompanying income or expenses upon receipt of the asset (with or without VAT).
4. In the tab "accounting" you need to fill in the asset accounting table - in accounting and tax accounting. The amount of the asset is indicated here, the method of write-off ... it can be not only write-off through depreciation, but for example, write-off to expenses, which can be specified here. You can also clarify VAT and additional transport other costs. Under the tables, you can select the "property tax" checkbox, in which case this tax will be applied to the asset.
5. In the "depreciation" tab you will find two sections - depreciation methods in accounting and tax accounting.
In accounting, you can choose one of 4 methods (linear, declining balance, cumulative or depreciation calculation - in proportion to the volume of production). You can also adjust the depreciation factor further (by default, the factor is 1).
In tax accounting, linear or non-linear depreciation is indicated. For non-linear depreciation, you can select the checkbox "use the indicator by group", and in this case, in the edit field, the depreciation rate in percent (from the general settings) is automatically set. Also, for non-linear depreciation, you can apply a special factor.
You can learn more about depreciation methods in the section "Methodology for accounting for fixed assets and other assets". In the Help, you will find detailed information about depreciation methods (formulas and calculation algorithms), useful lives, amortization periods, etc.
6. In the "modernization" tab, you must specify the period and cost of the upgrade, as well as the write-off method (through depreciation or costs). Additionally, you can specify a depreciation premium and increase the asset's useful life (in months).
7. In the "revaluation" tab for each year of the project, you can select the revaluation period, and in the edit field, specify the new cost after revaluation.
8. In the "conservation" tab from the list, select the start and end periods of conservation.
9. In the “disposal” tab, first of all, the method of disposal (write-off, sale or other disposal) is indicated, the period of disposal is also indicated. You can select the period of disposal of the asset - by default, that is, the "accounting period". And also, in the edit field, the cost of disposal is indicated, or the checkbox "disposal at residual value" is set. And in addition, you can specify the related income or expenses in the process of disposal of the asset.
10. Finally, after editing all assets, calculations can be performed. As in the other plans, here you can perform test calculations first or immediately perform the final calculation. Test calculations are performed at the planning stage when the final asset settings have not yet been determined and it is possible to view comparative calculation options.
11. If you want to perform a test calculation, click the “calculate” button and select the first or second item - “perform a test calculation of one asset” or “perform a test calculation of all assets in this depreciation group”. The result of test calculations is also displayed in the investment plan, and to perform a new test calculation, each time you need to clear the table (the "clear" button).
12. To perform the final calculation, click the "calculate" button and select the third item - "final calculation of the investment plan table - calculation of all assets". Click OK.
And now the calculation for each asset can be viewed in the tab “table of residual value”, where there is a calculation table. The table displays the data of accounting, tax accounting, and additionally shows the taxable difference, that is, the basis for calculating future deferred taxes. Here you can also enter a plan-actual deviation - that is, add updated data.
Detailed results of calculating all assets can be viewed in the "investment plan" table. Here you can see information about accumulated depreciation, the total residual value of all assets, accounting data - about purchases, upgrades, revaluations, and so on.
Deferred taxes are also presented here, these are deferred tax assets and deferred tax liabilities. A detailed algorithm for calculating deferred taxes can be found in the section "Methodology for accounting for fixed assets and other assets", there read "Algorithm for calculating deferred taxes" - how they are generated and where they are displayed in financial statements, etc.
13. Property tax is calculated separately from the calculation of assets. To do this, you just need to select the line "property tax" (click on the line) and click OK. After that, the results of calculating property tax will be displayed in the row.
☛ A detailed description of the calculation of property tax can be found in the section "taxes", there see the paragraph "algorithm for calculating property tax".
And finally, after the investment plan is built, when plans for accounting for fixed assets and other assets, investment assets are determined, property tax is calculated ... after that, the entire investment plan can be calculated, and it will be included in the final calculation of the business plan (Data → Calculate, or F9).
☛ Important! The calculation of the financial and investment plan is performed together with other financial plans - with statements of profit and loss, cash flow and balance sheet.